Describe the Structure of a Flagellum
Structure of Flagella and Cilia. Nine microtubule pairs surround another two pairs of microtubules in the center to form the core of the flagellum.
Flagella Definition Structure Types Arrangement Functions Examples
Describe the structure and function of a bacterial flagellum.

. It has a constant diameter and is made up of globular proteins the flagellin. 3 parts of Prokaryotic Flagellum. Of these nine are doublets.
Each cilium or flagellum consists of eleven microtubules. The flagella are helical in structure and composed of flagellin protein or globular protein. Eukaryotic flagella and cilia are identical in structure but have different lengths and functions.
Of these nine are doublets. 1 Cilia and flagella have fundamentally the same structures. In this article we will discuss about the Structure and Functions of Flagella and Cilia.
These are situated at the periphery and the remaining two are single microtubules situated in the centre. The flagellum in archaea is called the archaellum to note its difference from the bacterial flagellum. Flagella rotate counterclockwise to propel the cell forward and clockwise to tumble and change direction.
Bacterial flagellum is composed of three main parts that include. This is known as the nine-plus-two arrangement. If you were to remove all the organelles from a cell would the plasma membrane and the cytoplasm be the only components left.
What is the energy source for the flagellum. The Latin word flagellum means whip to describe its lash-like swimming motion. Movement is generated by a proton motive force PMF.
Flagella are longer 100-200 µm but fewer. These are situated at the periphery and the remaining two are single microtubules situated in the centre. -Bacterial flagellum fibrous appendage composed of protein subunits and anchored in the membrane.
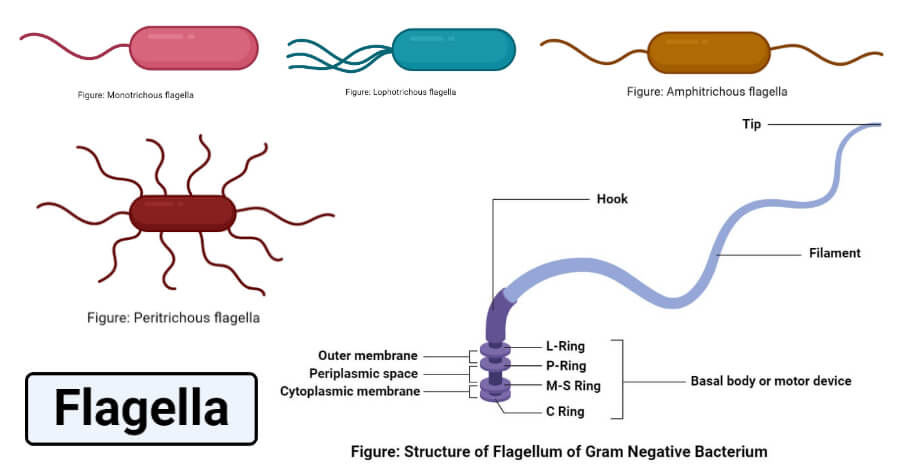
The axoneme usually has nine pairs of doublets of radially arranged peripheral microtubules and a pair of centrally located microtubules. If you compared two motile bacterial species and determined one was considerably more motile than the other which arrangement of flagella would you expect to be associated with the. Filament hook sheath and basal body.
Their main purpose is to increase the cell surface. How do bacterial flagella differ from archaella in. The body of flagella is divided into three parts.
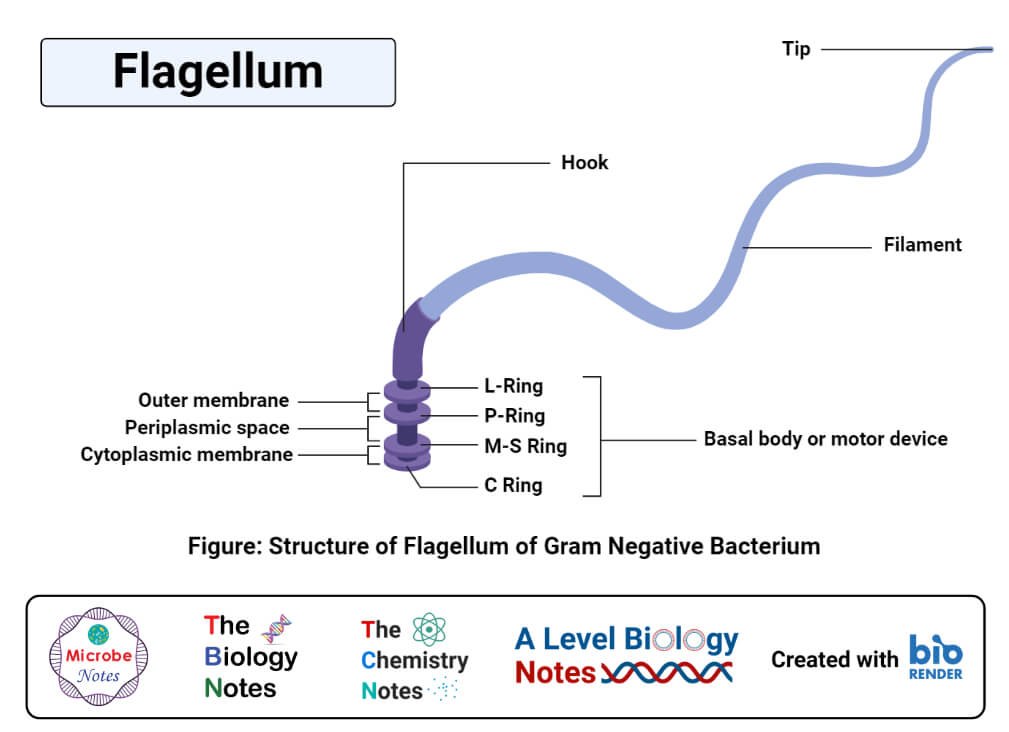
Basal body Anchors the flagellum to the cell wall and plasma membrane. Flagellum singular is hair like helical structure emerges from cell wall and cell membrane. Cilium and flagellum.
However the structure of the eukaryotic flagellum as well as the movement differs from the other types of flagella. The flagellum is a long cell protrusion capable of moving the entire cell. Explain the structure and function of cell membranes.
How do flagella generate cell motility. A flagellum has 3 parts. Their coordinated movements transport substances along the way.
Within the cytoplasm there would still be ions and organic molecules plus a. Thin 15-20nm in diameter. Describe the structure and functions of flagella and cilia.
The filament is inserted into the hook which is attached to the basal body. Basal structure Rotary motor Hook acts as the universal joint Filament the helical propeller. Cilia are cylindrical cell protrusions with microtubules inside.
Ii These microtubules are arranged in two radii. -Flagella rotate counterclockwise to propel the cell forward and clockwise to tumble and change direction. Cilium and flagellum.
Core of cilia and flagella is called the axoneme possesses a number of microtubules running parallel to the long axis. The basal body consists of a rod and a series of rings that are attached to the cell wall and the cytoplasmic membrane. Eukaryotes can contain one or multiple flagella moving in a whip-like motion.
The whole nine-plus-two structure is anchored in a basal body within the organism. The eukaryotic flagellum is a long rod-like structure that is surrounded by an extension of the cell membrane like a sheath. Eukaryotic flagella and cilia have a conserved common structure named the 92 structure in which nine doublet microtubules surround a pair of central singlet microtubules.
Single flagella can be seen with light microscope only after staining with special stain which increase the diameter of flagella. Describe the structure of a flagellum. Flagella is not straight but is helical.
Filament Contains the globular protein flagellin arranged in several chains that intertwine and form a helix around a hollow core 2. Each cilium or flagellum consists of eleven microtubules. Several axonemal components are found in the axoneme.
Microvilli are short but numerous cell protrusions. They are fine hair like movable protoplasmic processes of the cells which are capable of producing a current in the fluid medium for locomotion and passage of substances. The flagellins are arranged in several chains that intertwine and form a helix around a hollow core Fig.
It is responsible for motility of the bacteria. The flagellum is made up of microtubules composed from a protein called tubulin. I Cilia and flagella have fundamentally the same structures.
2 These microtubules are arranged in two radii. A bacterial flagellum is a fibrous appendage composed of protein subunits and anchored in the membrane. Hook Moves to help move flagella 3.
Radial spokes central apparatus and innerouter dynein arms which are the motors that drive the movement of cilia and flagella. The proteins of flagella act to identify certain pathogenic bacteria unlike eukaryotes the filaments are not covered by a membrane or sheath.
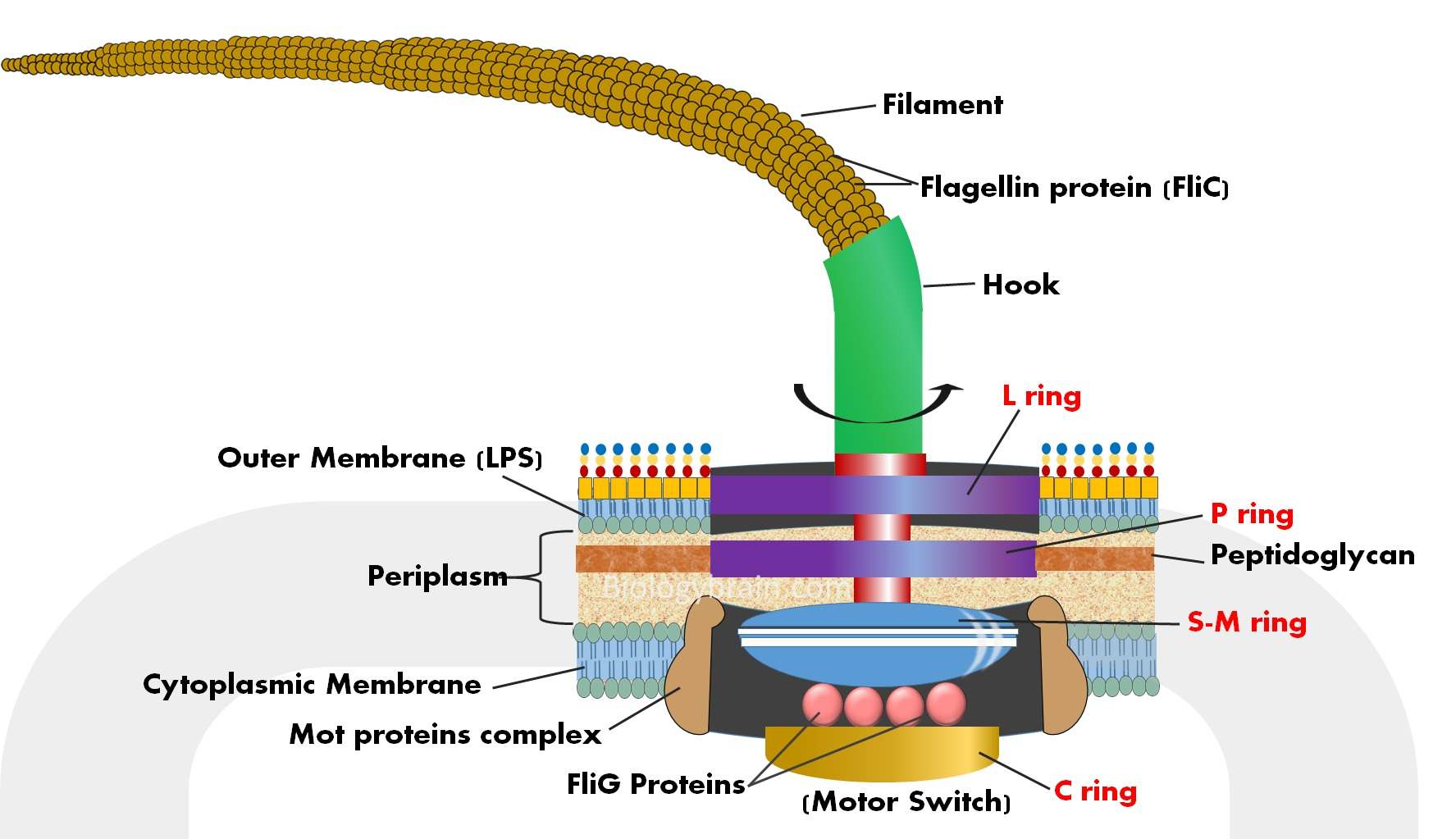
Diagram Of Flagella Definition Types Structure And Function Biology Brain

Schematic Diagram Of The Bacterial Flagellum The Flagellum Is A Download Scientific Diagram
Flagella Definition Structure Types Arrangement Functions Examples
Comments
Post a Comment